The easiest way to install language pack via Intune with PowerShell
The purpose of this blog post is to inform you how to install the language pack on Windows 10 or Windows 11 via Microsoft Intune. In this blog post, I list several different methods and then I will show my preferred ways.
There are several options to install the language pack via Microsoft Intune. When you have to deal with a multilingual environment, it could be hard to install the right language pack via Microsoft Intune. Especially when your users want or need to use Windows in their own language, but your global service desk is English-orientated. Also, not all languages are installed by the vendor, so you have to install the language via Intune. This can be a hard job when the users are all over the world, but I will explain my preferred way how to install the language pack via Intune easily.
Requirements:
Optional requirements:
Previously installation possibilities
There were several options available to install the language packs on Windows 10/11
- Manual installation via Settings
- Manual installation via Microsoft Store
- Manual or required installation via Company Portal, Microsoft Store, and PowerShell
Update from Microsoft
Since the 20h2 latest cumulative update, a new PowerShell command is available to install the language pack. I have tested this option, and this is awesome. I have already implemented this setting in multiple Intune environments. Also, I hear al lots of positive feedback in the community about this new method.
There are five PowerShell commands available to get, install, remove, or set the preferred language. It is easy to use, for example, to install a language pack use the following command:
Install-Language nl-NLThe PowerShell commands need to be run as an administrator and ask your users to run a PowerShell command is also not super user-friendly. Later more about this.
What are the new PowerShell commands?
| PowerShell commands | Description |
|---|---|
| Get-InstalledLanguage | Returns information about the installed languages on a device. |
| Get-SystemPreferredUILanguage | Returns the current System Preferred Language. |
| Install-Language | Installs a language onto a device. |
| Set-SystemPreferredUILanguage | Sets the provided language as the System Preferred UI Language. |
| Uninstall-Language | Uninstalls a language from a device. |
Note. Click here for all language pack tag
New installation possibilities
Today we have the below options available as well to install the language packs on Windows 10/11
- Manual or required installation via PowerShell (Install-Language)
- Required installation via Proactive remediation Script (Install-Language)
- Manual or required installation via Company portal, Win32App & PowerShell (Install-Language)
Which option should I use?
As you can see in the above list, there are several ways to install the language pack on Windows 10/11. formerly, I advised my customers to install the language pack manually because installing the language pack via Company Portal does not work properly. The language pack will be installed but will not appears in the list of available language. So, the user needs to run a PowerShell command in the user context. In my opinion not very user-friendly.
Also, I don’t like to tell the users you can install the language pack in the Microsoft store and your application in the Company Portal. I prefer one source of truth, and this is also not user-friendly in my opinion.
Of course, you can download the language pack and add a PowerShell script and wrap those files in a win32 app and distribute via Intune, but the PowerShell command will override the installed language(s) and default language. So, this is also not user-friendly.
So that was the reason why I always recommended installing the languages manually via settings. But now we have the new PowerShell command to install the language pack. This makes it easier to install the language packs.
The new PowerShell command is definitely my new preferred method. But depending on the organization’s preferences, I use the PowerShell, Proactive remediation, or Win32 app method via Intune. I will explain these three options in the sections below.
How to install language Pack via PowerShell script with Intune
PowerShell Script:
Install-Language nl-NL- Open Microsoft endpoint manager
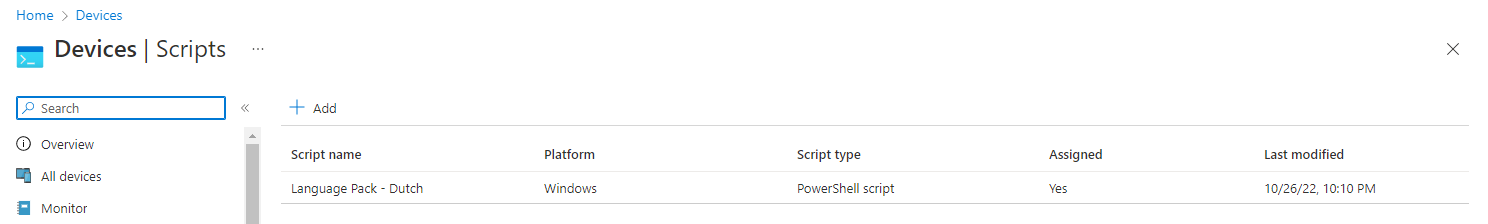
- In the menu select Devices
- Click on Scripts in the menu under Policy
Or use the following link Devices – Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center - Click on Add
- Select Windows 10 and later
- Provide a Nameg., Language Pack – Dutch
- Set a description if needed
- Click on Next
- Upload the PowerShell scripts
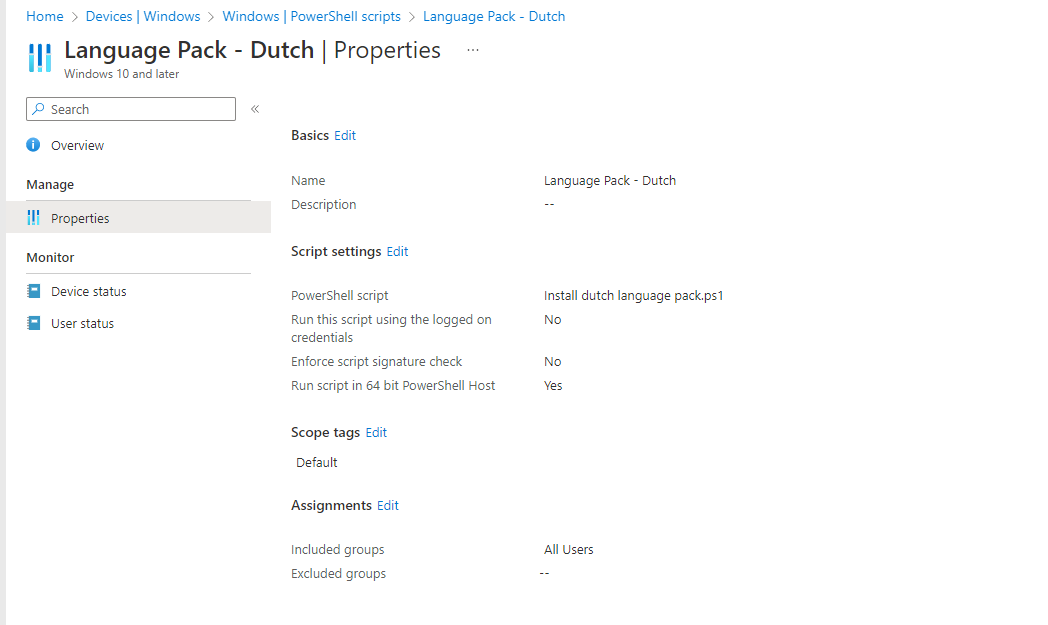
- Configure the following PowerShell script settings
| Settings | Value |
|---|---|
| Run this script using the logged on credentials | No |
| Enforce script signature check | No |
| Run script in 64 bit PowerShell Host | Yes |
- Set a scope tag if needed and click on next
- Assign the PowerShell script and click on Next
- Review the configuration and click on Add
How to install language Pack via Proactive Remediation script with Intune
Note. Save the PowerShell scrips as UTF8 encoded
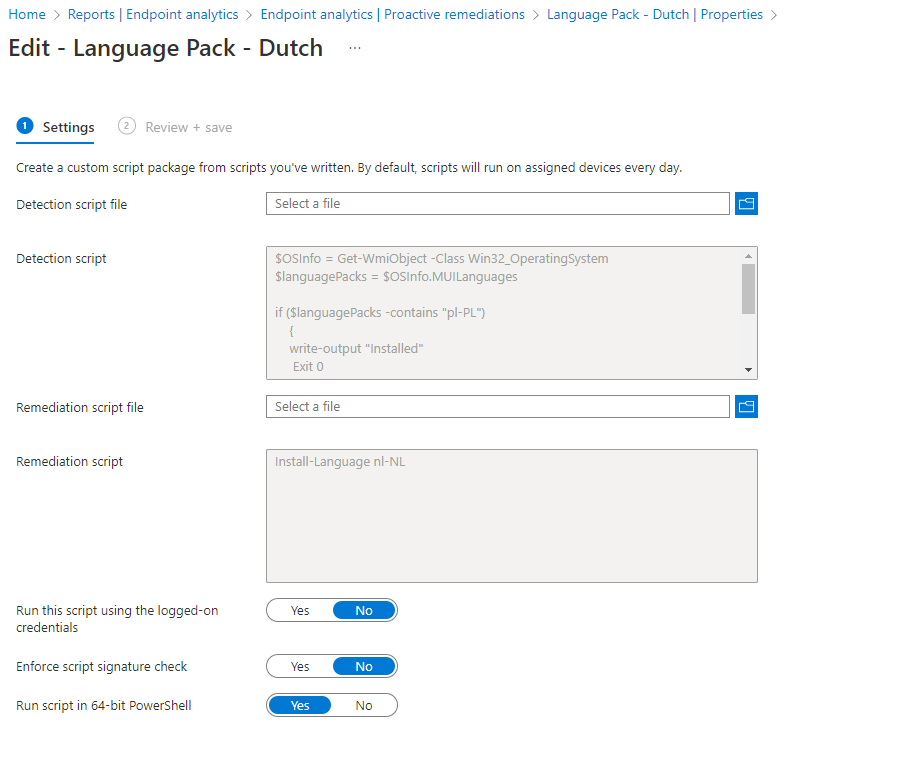
Detection script:
$OSInfo = Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_OperatingSystem
$languagePacks = $OSInfo.MUILanguages
if ($languagePacks -contains "nl-NL")
{
write-output "Installed"
Exit 0
}
else
{
write-output "Not installed"
Exit 1
}Remediation script:
Install-Language nl-NL- Open Microsoft endpoint manager
- In the menu select Reports
- Click on Endpoint analytics in the menu under Analytics
- Click on Proactive remediations
Or use the following link Endpoint analytics – Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center - Click on Create script package
- Provide a Nameg., Language Pack – Dutch
- Set a description if needed
- Click on Next
- Upload the Detection scripts and Remediation scripts.
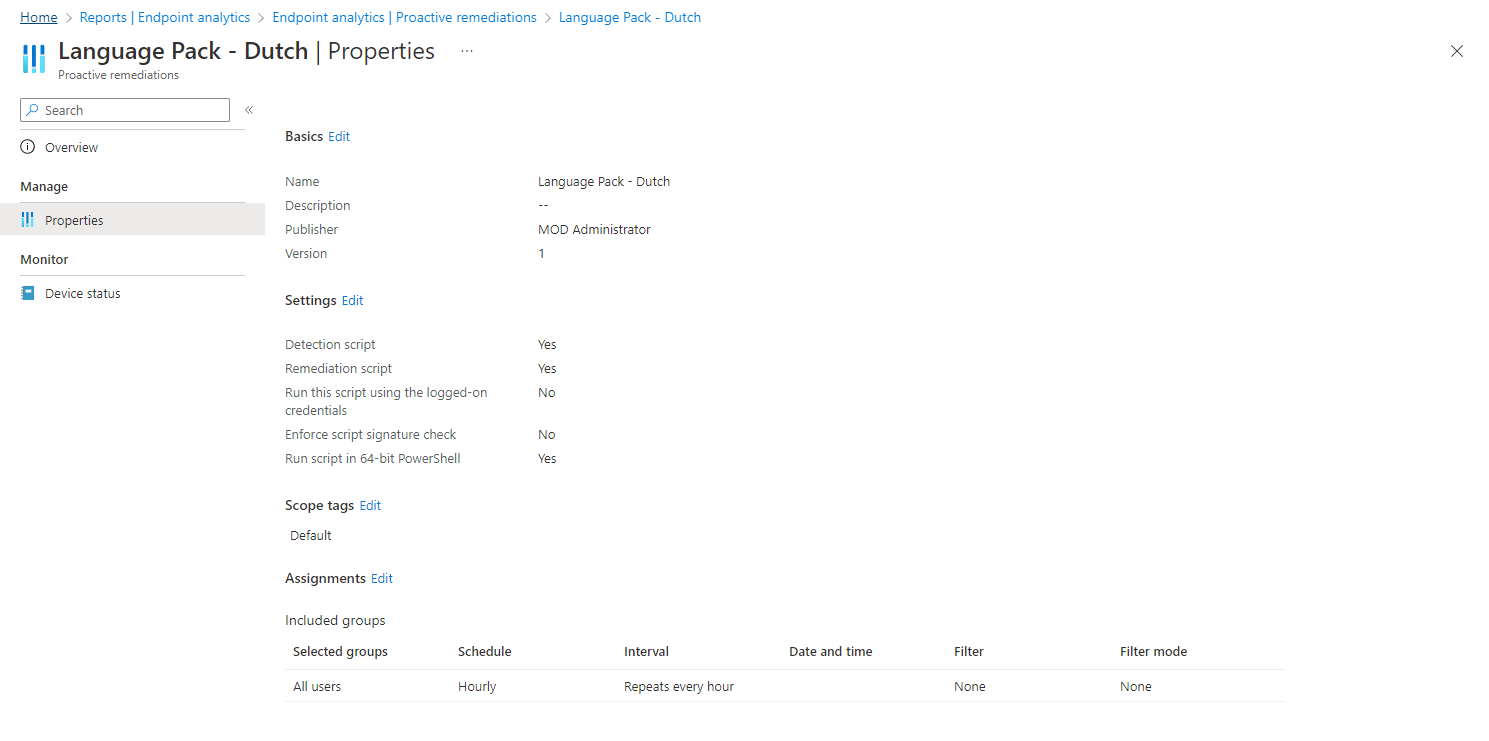
- Configure the following Proactive remediation script settings
| Settings | Value |
|---|---|
| Run this script using the logged on credentials | No |
| Enforce script signature check | No |
| Run script in 64 bit PowerShell Host | Yes |
- Click on Next
- Set a scope tag if needed and click on next
- Assign the Proactive remediation script
- Now we must change the schedule via the 3 bullets and click on Edit
- Click on the dropdown list and change the frequency from Daily to Hourly and click on Apply
- Click on next
- On the Review + create section, check the configuration, and click on Create
How to install language pack via Company portal via Intune
Install script (Install Dutch language pack.ps1)
Install-Language nl-NLUninstall script (Uninstall Dutch language pack.ps1)
Uninstall-Language nl-NL- Create an empty folder and place the above PowerShell scripts in the folder.
- Create the .intunewin package with the Intune content preparation tool with the following command:
{directory of WinappUtil}\IntuneWinAppUtil.exe -c { directory of Language pack files } -s Install Dutch language pack.ps1 -o .\ -qNote. Click here to download the Win32 content prep tool
- Now we have the installer with the install and uninstall PowerShell Script we are ready to upload the installer to Intune
- Open Microsoft Intune
- In the menu select Apps
- Under Apps, select Windows
Or use the following link Windows Apps – Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center - Click on + Add
- Select the App Type Windows App (Win32) and click on Select
- Click on the Select app package file and click on the blue directory icon
- The file explorer will be opened and browse to the .Intunewin installer file that you have created.
- Click on OK
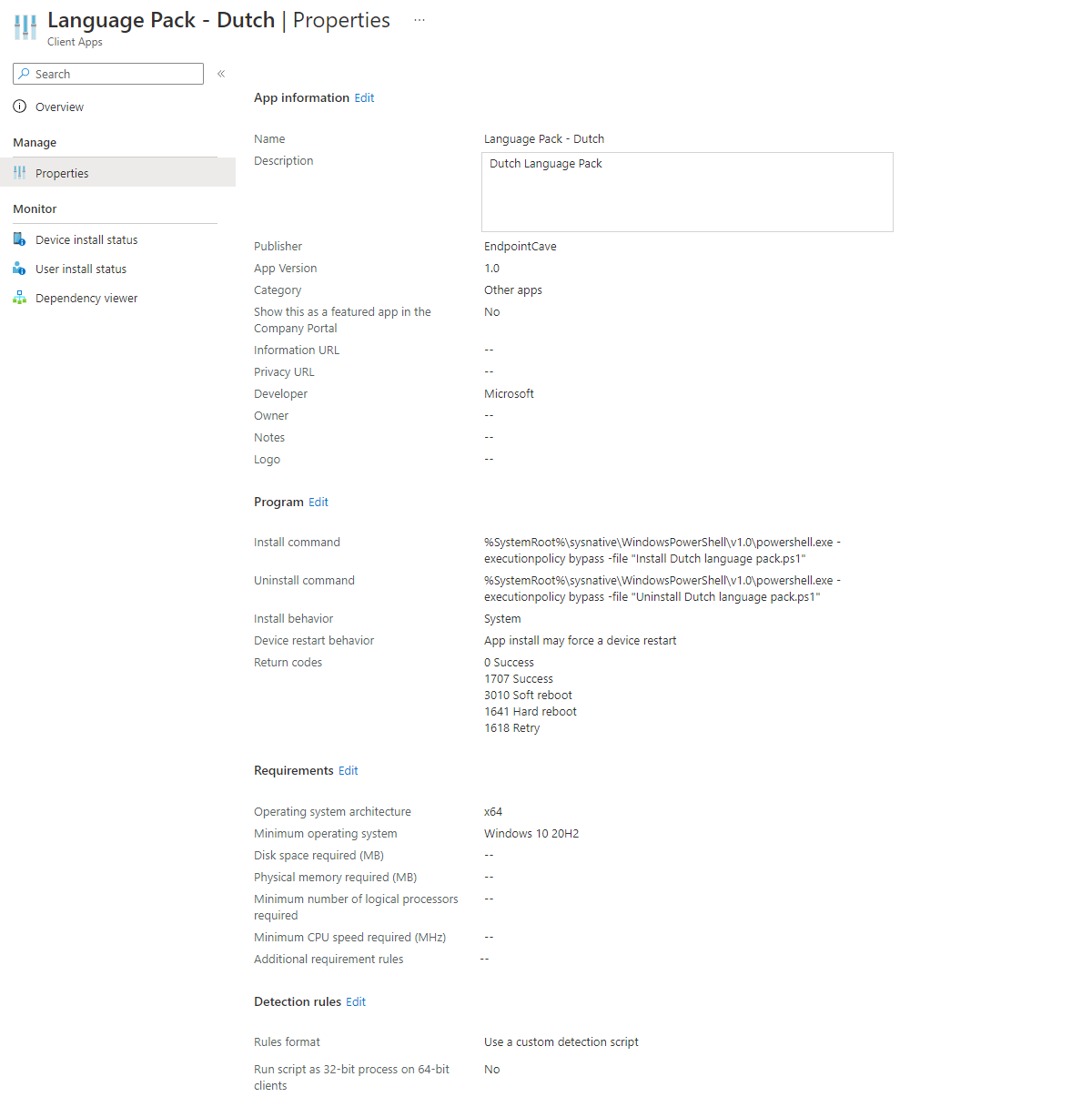
- Set the required name, description, and publisher fields and if needed other optional fields
- Click on Next
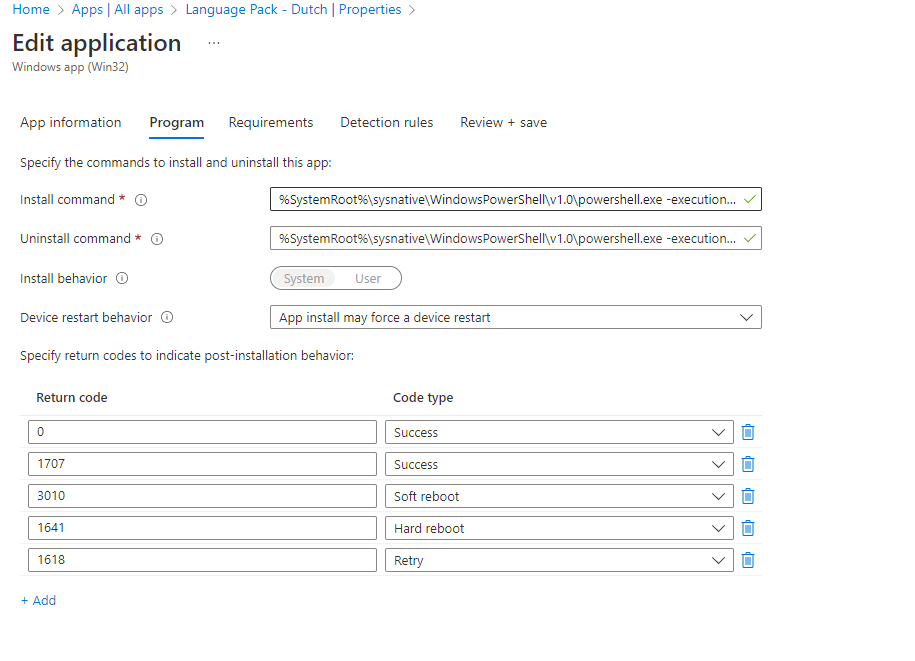
- Set the following Install and uninstall commands
Install command:
%SystemRoot%\sysnative\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe -executionpolicy bypass -file "Install Dutch language pack.ps1"Uninstall command:
%SystemRoot%\sysnative\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe -executionpolicy bypass -file "Uninstall Dutch language pack.ps1"- On the requirements section. Select 64-bit as the operating system architecture and Windows 10 20H2 as the minimum operating system and click on next
- Select Use a custom detection script as the rules format on the Detection rules section
- Upload a detection script
Script:
$OSInfo = Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_OperatingSystem
$languagePacks = $OSInfo.MUILanguages
if ($languagePacks -contains "nl-NL")
{
write-output "Installed"
Exit 0
}
else
{
write-output "Not installed"
Exit 1
}- Set both PowerShell script options (Run script as 32-bit process on 64-bit clients and Enforce script signature check and run script silently) to No
- Click on Next on the Dependencies section and on Supersedence section click next as well
- Set a Scope tag if needed and click on Next
- Assign the application as available or required
- Click on next. Check the app configuration and click on Create
- The Language Pack app will be created and uploaded and ready to install




Dear René
Wonderful guide!
I was wondering if you might have an advice on installing different language packs automatically during the Intune Autopilot. For example, Intune autopilot running in Germany, France and in the UK but once done regional setting, keyboard and language needs to be changed manually. Is it possible to automate language pack installs, regional settings and keyboard for different regions (time zones) during the autopilot perhaps via Powershell and Win32 app or maybe via some other method(s)?
Dear René,
Could you, by any chance, in a future blog post, expand this and add the setting/overwritting of all the language settings?
Hi Glenn,
If you want to overwrite the language settings you can change the script to
Install-Language nl-NL
Set-SystemPreferredUILanguage nl-NL
Set-SystemLanguage nl-NL
Kind regards,
Rene
Thanks for the very informativ blog post.
I tried to install the language pack with PowerShell, but it’s not working at all..
Even if I try to install it directly on the client it get the following error message: “Language pack or features could only be partially installed. ErrodCode: -2147024891. Please try again..”
Anyone having the same or any solutions?
Hi Hans,
Which option are you using?
Did you run it as an Administrator?
Which language do you want to install?
What OS and version are you using?
Sure..
Started the PowerShell Console manually as an Administrator and typed: Install-Language fr-CH (and also others like it-IT or it-CH)
The installation is starting and running for a long time, till running into a failure.
Any suggestion?
Same thing happening with me. This is the script I used to kill the process but install the language:
$timeoutSeconds = 60
$job = Start-Job -ScriptBlock {
Install-Language es-ES
}
Wait-Job $job -Timeout $timeoutSeconds | out-null
if ($job.State -eq “Completed”) {Write-Output “done!” }
elseif ($j.State -eq “Running”) { Write-Output “interrupted” }
else { Write-Output “Unknown Error” }
Remove-Job -force $job
$OSInfo = Get-WmiObject -Class Win32_OperatingSystem
$languagePacks = $OSInfo.MUILanguages
if ($languagePacks -contains “es-ES”)
{
write-output “Installed, this device has: $languagePacks”
Exit 0
}
else
{
write-output “Not installed, this device has: $languagePacks”
Exit 1
}
Hello Rene,
I am trying to install the English Australia language pack with no luck.
Can you please advise?
Hi Anup, what did you try ?
I have tried using your proactive remediation script to install Australia english en-AU however,it failed to install.
can you please help how can I install en-AU with proactive script and also set the en-AU as a default.
when running the install-language command on windows 11 22h2 it says that the term is not recognized? any reaosn why? i have powershell 5.1, is powershell 7 required?
Hi Jourdan, is your device up to date? are all the updates installed on your device?
Kind regards,
Rene
I’ve seen this happen as well. There is an issue. Unfortunately I have not found a fix, other than to wrap the command in an intunewin.
Hi There,
I have a strange issue, as I am trying to run install-language as a task sequence PowerShell script step. Even tough I can see the language pack management files in the system32 module folder ( I assume it means its installed) and I import the module. When I run the command install-language I receive an error install-language is not recognized. Will the command run as system account or do we need to run it as admin user. Pls guide me further.
Hi yuva, you can run it as both users, intune runs the scripts via the system account but when I install it from PowerShell it will runs under my admin account.
Which version of windows are you using because there are some specific versions and update required.
Are you using mdt of sccm to install the language pack and in which phase ?
Nice René, thanks for the effort, helps me out a lot!
I’ve tried running install-language on 21H2 and it doesn’t work. Can you give more information on this?
Hi Dan, did you get any error code in PowerShell? Did you run it as an Administrator?
Would you please share the total command?
Kind regards,
Rene